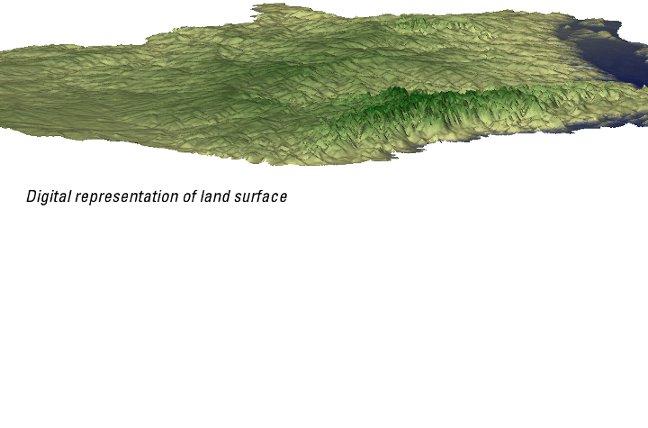
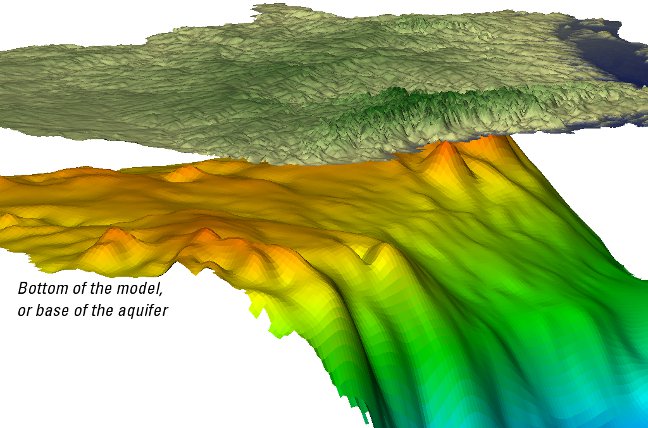
While many different types of models exist, the primary model referred to in this study will be a numerical model. Using the USGS MODFLOW software, information about the geology, water use, and streams (among many other types of data) are compiled into a 3D numerical representation of the system. Modelers often begin with the framework, or 3D layers representing the aquifers and confining units in the subsurface and add information about how water moves through each of the layers.
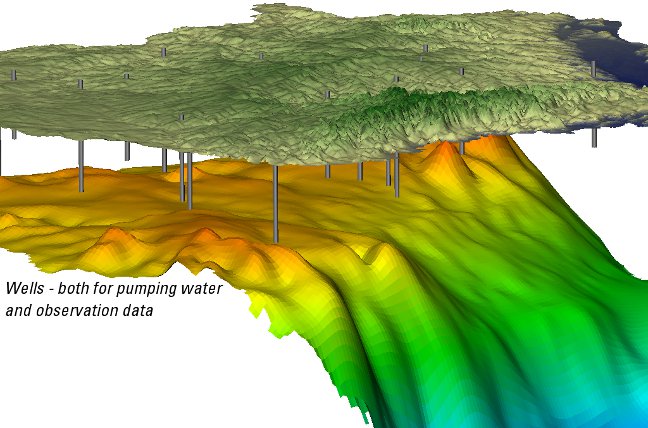
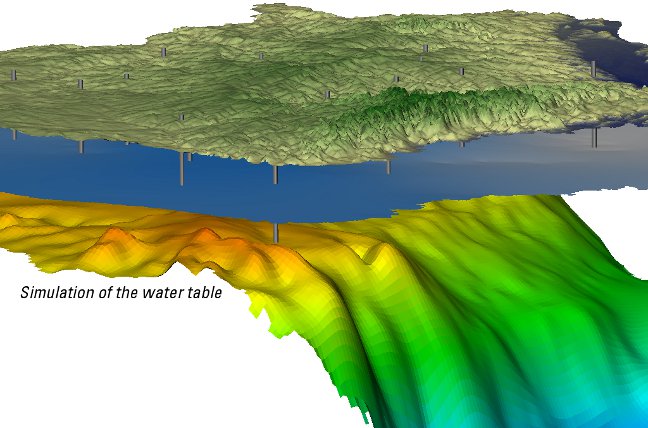
In order to test if the model represents the groundwater system, observation data is used to compare the model with data gathered in the field. The majority of this data for a groundwater model is often water levels measured from wells - all in different areas and measured at different times.
The amount or quality of groundwater used for human consumption or agriculture is of typical concern when developing a groundwater model. Compiling water use is often a difficult task because the amount and timing of the pumping of groundwater is not well documented, particularly for agricultural purposes.
See Also
For more information on the USGS Regional Groundwater Studies, please visit the USGS Groundwater Resources Program.